音響信号処理全般でよく用いられるスペクトログラムを、Pythonで時間波形から変換する方法について見ていきます。ここでは、PyTorchのtorchaudio.transforms.Spectrogramと、librosaのlibrosa.stftを用います。
スペクトログラムに変換するサンプル音源を、以下コードを実行して、_sample_dataフォルダにダウンロードします。また、スペクトログラム表示用の関数plot_spectrogramを定義します。
import os
import requests
import librosa
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 音声の保存
_SAMPLE_DIR = "_sample_data"
SAMPLE_WAV_URL = "https://pytorch-tutorial-assets.s3.amazonaws.com/VOiCES_devkit/source-16k/train/sp0307/Lab41-SRI-VOiCES-src-sp0307-ch127535-sg0042.wav"
SAMPLE_WAV_PATH = os.path.join(_SAMPLE_DIR, "speech.wav")
os.makedirs(_SAMPLE_DIR, exist_ok=True)
with open(SAMPLE_WAV_PATH, 'wb') as f:
f.write(requests.get(SAMPLE_WAV_URL).content)
# スペクトログラム表示用関数
def plot_spectrogram(spec, title=None, ylabel="freq_bin", aspect="auto", xmax=None):
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 1)
axs.set_title(title or "Spectrogram (db)")
axs.set_ylabel(ylabel)
axs.set_xlabel("frame")
im = axs.imshow(librosa.power_to_db(spec), origin="lower", aspect=aspect)
if xmax:
axs.set_xlim((0, xmax))
fig.colorbar(im, ax=axs)
plt.show(block=False)
torchaudio.transforms.Spectrogramの使い方
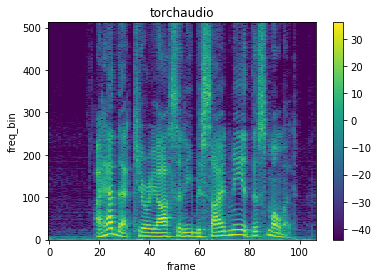
PyTorchでは、torchaudio.transforms.Spectrogramを使うことでスペクトログラムに変換できます。
先ほど、ダウンロードした音声ファイルを読み込んで、スペクトログラムに変換します。パラメータの、n_fftにはfftのサイズ、win_lengthには窓関数のサイズ、hop_lengthにはスライドさせるサイズ、window_fnには窓関数を指定します。PyTorchでは、Bartlett window、Blackman window、Hamming window、Hann window、Kaiser windowが用意されています。
- 関連記事 – PyTorchで音声/音楽データを読み込むtorchaudio.load
- torchaudio.transforms.Spectrogram – v 0.11.0 Torchaudio Documentation
- PyTorchで用意されている窓関数 – v 1.11.0 PyTorch Documentation
import torch
import torchaudio
import torchaudio.transforms as T
waveform, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(filepath=SAMPLE_WAV_PATH)
n_fft = 1024
win_length = None
hop_length = 512
window_fn = torch.hann_window
spectrogram = T.Spectrogram(
n_fft=n_fft,
win_length=win_length,
hop_length=hop_length,
window_fn=window_fn,
power=2.0,
)
spec = spectrogram(waveform)
plot_spectrogram(spec[0], title='torchaudio')
librosa.stftを用いたスペクトログラムへの変換
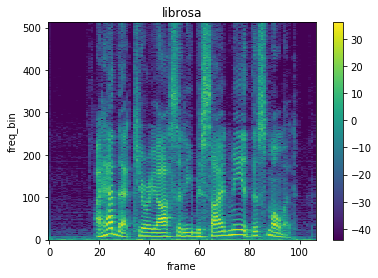
librosaではlibrosa.stftを使うことでスペクトログラムに変換できます。PyTorchと同じでパラメータの、n_fftにはfftのサイズ、win_lengthには窓関数のサイズ、hop_lengthにはスライドさせるサイズ、window_fnには窓関数を指定します。窓関数は、SciPyのscipy.signal.windowsから選択することができます。
librosa.stftの戻り値は、短時間フーリエ変換の複素数行列であるので、今回はPyTorchと揃えるために、絶対値の二乗をしてパワーに変換しています。
- 関連記事 – librosaで音声/音楽データを読み込むlibrosa.load【Python】
- librosa.stft – librosa API documentation
- Window functions – SciPy API reference
import numpy as np
waveform, sample_rate = librosa.load(SAMPLE_WAV_PATH, sr=None, mono=False)
n_fft = 1024
win_length = None
hop_length = 512
window_fn = 'hann'
spec = np.abs(librosa.stft(y=waveform, n_fft=n_fft, hop_length=hop_length, win_length=win_length, window=window_fn))**2
plot_spectrogram(spec, title='librosa')

コメント